- Vanessa Arrieta Paniagua, predoctoral researcher at the Translational Cardiology Unit of Navarrabiomed - IdiSNA will present her doctoral thesis by the Public University of Navarra next Monday, November 28, at 12:00, in the Assembly Hall of Navarrabiomed.
The doctoral work, entitled "Role of sST2 in myocardial fibrosis in severe aortic stenosis”, has been developed at the University Hospital of Navarra and Navarrabiomed under the direction of Natalia López Andrés, Principal investigator of the Translational Cardiology Unit.
Aortic stenosis is the most common valvular heart disease in Europe and North America affecting 2-7%, depending on the region, in population over 65 years of age. To date, there is no medical treatment that can slow down or reverse the evolution of the disease, so aortic valve replacement (surgical or percutaneous) is the only treatment when symptoms or ventricular dysfunction appear.
This disease produces an abnormal progressive narrowing of the aortic valve that, as a result of pressure overload, causes hypertrophy of the left ventricle. In this process, myocardial fibrosis has an important pathophysiological role, as well as a prognostic role. Initially, myocardial fibrosis is part of a compensatory mechanism, but in advanced stages a focal replacement fibrosis appears, leading to ventricular dysfunction and heart failure. The pathophysiological mechanisms underlying these processes are not fully understood.
Focal replacement fibrosis can be detected and quantified by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with the delayed enhancement (DE) sequences. The presence of DE in patients with severe aortic stenosis has been shown to be an independent predictor of mortality and unfavourable clinical outcome in this group of patients. However, MRI is an expensive technique with limited availability, so it is not used in the follow-up of this group of patients in routine clinical practice.
The hypothesis of this thesis is that as the levels of soluble ST2 (sST2), a biomarker associated with the process of fibrosis and myocardial remodelling, are elevated in case of aortic stenosis, they may have a prognostic value. Specifically, this study addresses the role of sST2 in myocardial fibrosis in severe aortic stenosis.
Research development
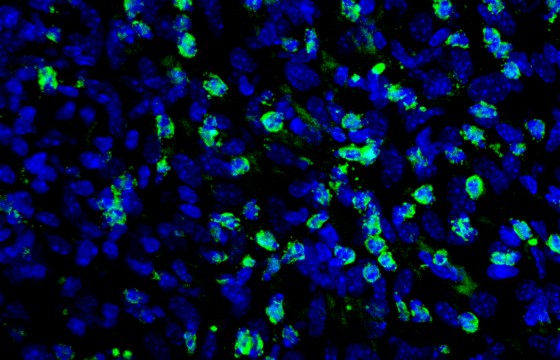
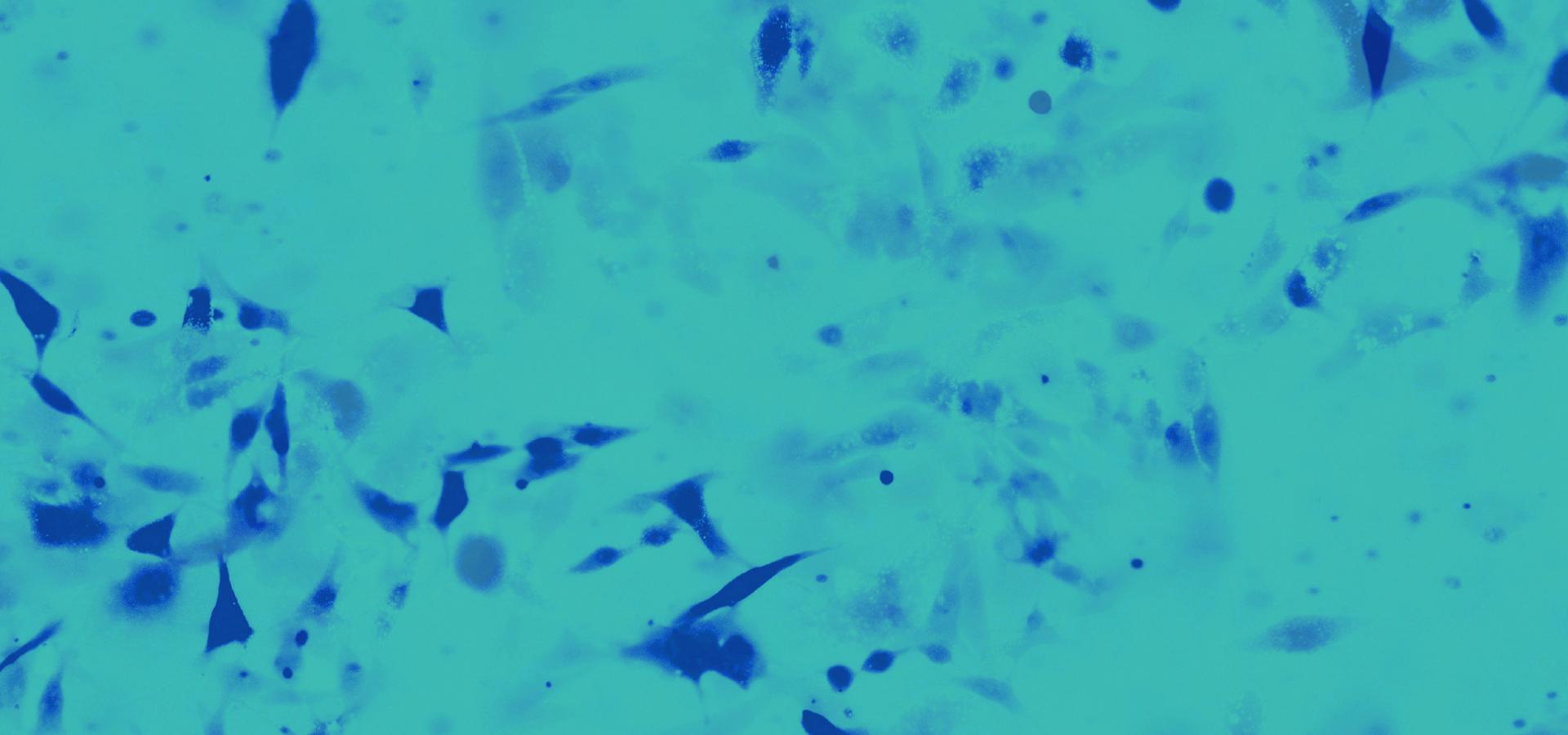
The work is proposed from a translational point of view, and has a dual goal. First of all, to delve into the pathophysiological role of tSS2 in severe aortic stenosis. To this end, a proteomic study has been carried out to assess the proteins modulated by sST2 in human cardiac fibroblasts and the in vitro effects of sST2 on human cardiac fibroblasts have been investigated. The results have been validated in vitro in a rat model with pressure overload and in myocardial biopsies of patients with aortic stenosis that underwent surgery.
Likewise, it has been demonstrated that sST2 exerts a deleterious role in human cardiac fibroblasts, on the one hand, affecting the mitochondrial function of the cell and thus increasing oxidative stress and the synthesis of proinflammatory molecules and on the other hand, promoting differentiation to myofibroblasts and increasing the synthesis of profibrotic molecules. These findings were validated in the animal model and in myocardial biopsies of patients with aortic stenosis.
Secondly, from the clinical point of view, a cohort of patients with severe aortic stenosis with surgical indication was analysed to check if the blood levels of sST2 are associated with the DE evaluated by MRI in patients with severe aortic stenosis. Thus, it is observed that patients with severe aortic stenosis with cardiac MRI DE have significantly higher blood levels of sST2 than those without RT. Blood sST2 levels are positively correlated with DE mass and with VI mass in patients with severe aortic stenosis. High levels of sST2 make it possible to identify patients with severe aortic stenosis with DE, without having to perform cardiac MRI, in a simple way that can be applied in routine clinical practice.
Dissemination of results
The work carried out has led to several scientific publications: in 2019, in the journal Clinical Science, “Soluble ST2 promotes oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiac fibroblasts: an in vitro and in vivo study in aortic stenosis”, and in 2020 in the journal Cells, “Soluble St2 Induces Cardiac Fibroblast Activation and Collagen Synthesis via Neuropilin-1”.
In addition, the results have been disclosed at several national and international congresses such as the SEC Congress in Bilbao (in 2015 and in 2017), at the 29th EACTS Annual Meeting in Amsterdam, in 2015 or at the Heart Failure Congress in Paris, in 2017.