El nuevo proyecto europeo HEALCIER buscará junto a centros sanitarios oportunidades para un uso más eficiente y eficaz de los recursos a través de la Economía Circular

- El objetivo principal del proyecto es mejorar la competitividad de la cadena de valor de la asistencia sanitaria mediante la implantación de los principios de la economía circular.
Azaro Fundazioa, junto al Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria BIOCRUCES BIZKAIA, El Centro de Investigación Biomédica Navarrabiomed, AIN (Asociación de la Industria Navarra) y ESTIA (Ecole Supérieure des Technologies Industrielles Avancées), lidera el nuevo proyecto europeo HEALCIER, con el objetivo principal de mejorar la competitividad de la cadena de valor de la asistencia sanitaria mediante la implantación de los principios de la economía circular.
El proyecto, que tendrá un año de duración, está cofinanciado al 65% por el Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER) a través del Programa INTERREG POCTEFA, y cuenta además con la estrecha colaboración de OSI Ezkerraldea Enkarterri Cruces y el Complejo Hospitalario de Navarra.
El sector sanitario y el consumo de recursos
El envejecimiento en el área transfronteriza está ejerciendo una importante presión sobre el sistema sanitario al incrementarse la demanda del servicio tanto en términos de cantidad como de calidad. Este incremento de la demanda ejerce, asimismo, presión sobre el sector incidiendo en una mayor utilización de los recursos.
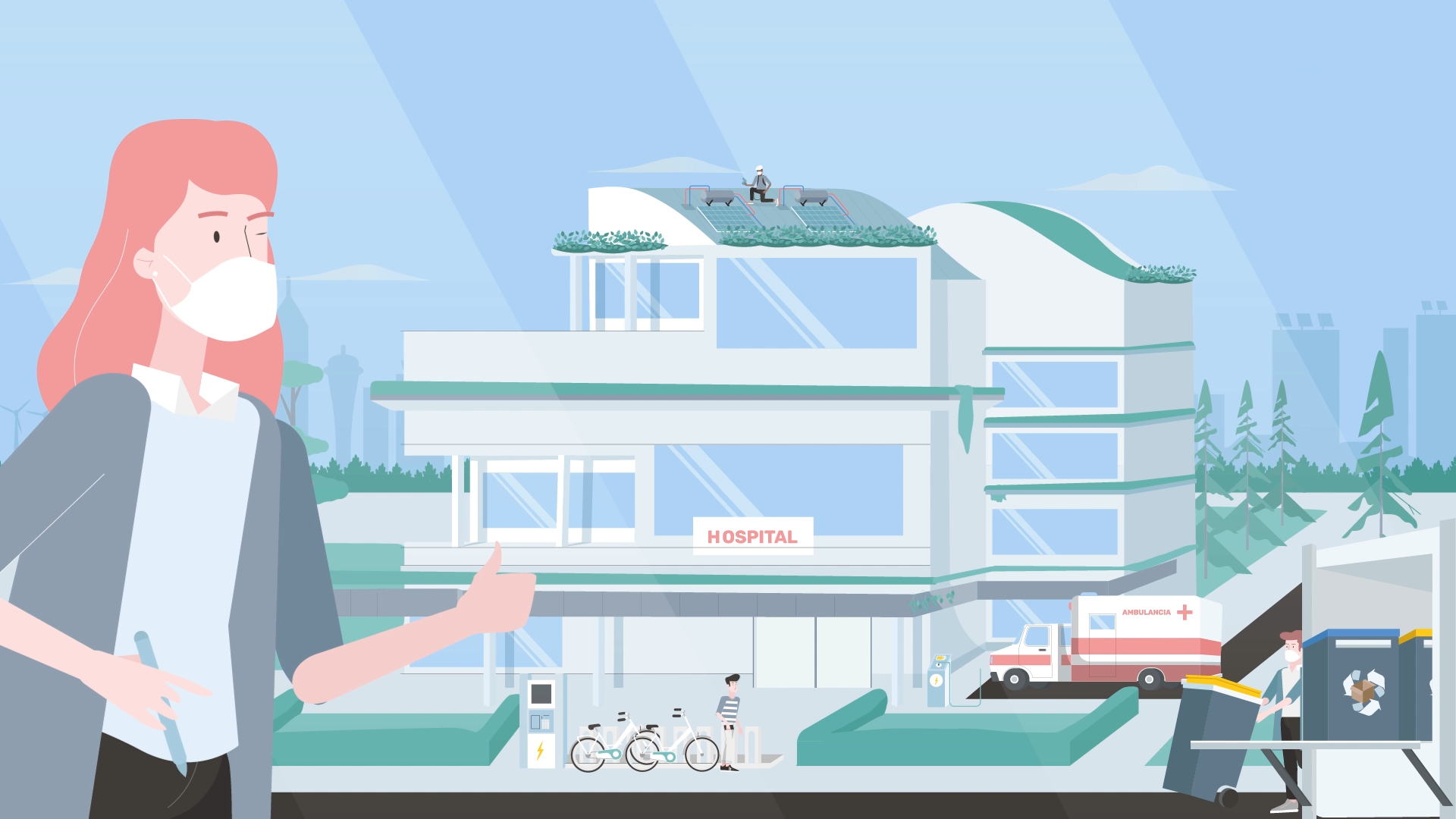
El sector sanitario es, en consecuencia, uno de los sectores de mayor consumo de recursos (agua, energía, alimentación, materias primas, productos terminados, etc…) con un impacto importante en la sostenibilidad ambiental. Además, genera un alto volumen de residuos por el uso generalizado de productos de un solo uso: guantes, jeringas, residuos radiactivos, fármacos no usados, pruebas o tratamientos innecesarios, mantenimiento de dispositivos, etc.
Un gran hospital en números
Para hacernos una idea, la media de consumo anual de energía térmica, eléctrica y de gas que realiza un gran hospital supera los 50 millones de kWh. La cantidad de residuos que genera traspasa fácilmente las 2.000 toneladas de las que tres cuartas partes pertenecen a residuos no peligrosos (residuos urbanos, papel y cartón, plástico, tóneres, aceites alimentarios, escombros…), y una cuarta parte a residuos peligrosos (sanitarios tipo II, citostáticos, líquidos laboratorio, baterías y pilas, radiografías, envases de productos peligrosos…).
3 millones de jeringuillas, 14 millones de guantes, 2.000 toneladas de ropa lavada, 175.000 m3 de agua… son aproximadamente los números que se manejan en un hospital grande que atiende aproximadamente a 3 millones de pacientes al año. El ámbito sanitario consume muchos recursos, y por ello, a su vez es un sector que puede aportar también muchas oportunidades para desarrollar actividades económicas relacionadas con un uso más eficiente y de aprovechamiento de dichos recursos.
HEALCIER, un proyecto basado en la Economía Circular
La Economía Circular (EC) ha sido identificada como una herramienta adecuada por la Comisión Europea para promover un uso más eficiente de los recursos mientras se promueve una mayor competitividad, dado que favorece el desarrollo de actividades económicas más innovadoras y sostenibles, aprovechando los recursos locales disponibles.
Por ello, HEALCIER pretende contribuir a mejorar la competitividad del sector sanitario aplicando la economía circular. Se trata de impulsar un uso más eficiente y eficaz de los recursos en los centros sanitarios con el fin de fomentar un sector sanitario más innovador y competitivo que disponga de un menor impacto ambiental.
Las fases del proyecto serán cuatro:
- Se desarrollará una metodología para la medición del impacto de la implementación de los principios de la EC en el ámbito de la asistencia sanitaria.
- Los socios, utilizando la metodología desarrollada, realizarán un diagnóstico de las oportunidades y potencialidades de la EC en cada uno de los centros hospitalarios participantes en el proyecto. Estos diagnósticos servirán para identificar las oportunidades existentes para que las diferentes empresas que conforman la cadena de valor puedan desarrollar nuevos modelos de negocio o actividades económicas. Los diagnósticos permitirán identificar adicionalmente empresas que puedan proporcionar soluciones aplicando la economía circular.
- Con los datos obtenidos cada región elaborará un mapa de oportunidades para el desarrollo de nuevas actividades y modelos de negocio aplicando la EC.
- Finalmente, se valorará las posibilidades que las empresas tienen de desarrollar soluciones relacionadas con las oportunidades identificadas y se definirán potenciales colaboraciones con otras empresas o centros tecnológicos de la Eurorregión para aplicar soluciones.
El proyecto ha sido cofinanciado al 65% por el Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER) a través del Programa Interreg V-A España-Francia-Andorra (POCTEFA 2014-2020). El objetivo del POCTEFA es reforzar la integración económica y social de la zona fronteriza España-Francia-Andorra. Su ayuda se concentra en el desarrollo de actividades económicas, sociales y medioambientales transfronterizas a través de estrategias conjuntas a favor del desarro